Convolution Theorem Laplace Transform Examples
Characteristics of the Phase. It completely describes the discrete-time Fourier transform DTFT of an -periodic sequence which comprises only discrete frequency componentsUsing the DTFT with periodic dataIt can also provide uniformly spaced samples of the continuous DTFT of a finite length sequence.

Inverse Laplace Transforms As Convolutions Youtube
Transforms and the Laplace transform in particular.

. In this section we will examine how to use Laplace transforms to solve IVPs. Evaluation of Convolution Integral. However Fs is too complicated to fit with.
Ft gt be the functions of time t then First shifting Theorem. Sampling the DTFTIt is the cross correlation of the input sequence and a complex sinusoid. Z-transform may exist for some signals for which Discrete Time Fourier Transform DTFT does not exist.
The time function ft is obtained back from the Laplace transform by a process called inverse Laplace transformation and denoted by -1. The examples in this section are restricted to differential equations that could be solved without using Laplace transform. Res σ o.
The advantage of starting out with this type of differential equation is that the work tends to be not as involved and we can always check our answers if we wish to. Periodic Nature of the DFT. If xt is absolutely integral and it is of finite duration then ROC is entire s-plane.
Transforms and the Laplace transform in particular. Simplify Fs so that we can identify the inverse Laplace transform formula for each part of Fs from the Laplace inverse table. Step Functions In this section we introduce the step or Heaviside function.
In other words given a Laplace transform what function did we originally have. Renumbered from ECE 207. Suppose that you want to find the inverse transform xt of Xs.
Cross-listed with BENG 280A. If youre seeing this message it means were having trouble loading external resources on our website. Learn for free about math art computer programming economics physics chemistry biology medicine finance history and more.
Examples from optical imaging CT MR ultrasound nuclear PET and radiography. ROC contains strip lines parallel to jω axis in s-plane. If you can write Xs as a product FsGs where ft and gt are known then by the above result xt f gt.
Convolution via the Frequency Domain. Fs s 19 s 2 3s 10 Solution. Convolution is a very powerful technique that can be used to calculate the zero state response ie the response to an input when the system has zero initial conditions of a system to an arbitrary input by using the impulse response of a system.
Concept of Z-Transform and Inverse Z-Transform Z-transform of a discrete time signal xn can be represented with XZ and it is defined as. Inverse Laplace Transform Example with Partial Fractions Decomposition. The range variation of σ for which the Laplace transform converges is called region of convergence.
The main properties of Laplace Transform can be summarized as follows. Let C 1 C 2 be constants. Laplace transform is the integral transform of the given derivative function with real variable t to convert into a complex function with variable s.
Multiplying Signals Amplitude Modulation The Discrete Time Fourier Transform. Visit BYJUS to learn the definition properties inverse Laplace transforms and examples. Khan Academy is a nonprofit with the mission of providing a free world-class education for anyone anywhere.
Compression and Expansion Multirate methods. The Convolution Theorem If the Laplace transforms of ft and gt are Fs and Gs respectively then Lf gt FsGs 12 that is L1 FsGs f gt. The first equation is the one dimensional continuous convolution theorem of two general continuous functions.
If xt is a right sided sequence then ROC. Linearity of the Fourier Transform. We again work a variety of examples illustrating how to use the table of Laplace transforms to do this as well as some of the manipulation of the given Laplace transform that is needed in order to use the table.
Properties of ROC of Laplace Transform. The convolution theorem is also one of the reasons why the fast Fourier transform FFT algorithm is thought by some to be one of the most important algorithms of the 20 th century. It uses the power of linearity and superposition.
Use the inverse Laplace to find ft. Fourier Transform Pairs. Fundamentals of Fourier transform and linear systems theory including convolution sampling noise filtering image reconstruction and visualization with an emphasis on applications to biomedical imaging.
The second equation is the 2D discrete convolution theorem for discrete. In mathematics the Laplace transform named after its discoverer Pierre-Simon Laplace l ə ˈ p l ɑː s is an integral transform that converts a function of a real variable usually in the time domain to a function of a complex variable in the complex frequency domain also known as s-domain or s-planeThe transform has many applications in science and engineering because.

Csir Ugc Net Convolution Theorem In Laplace Transform Part 1 Offered By Unacademy
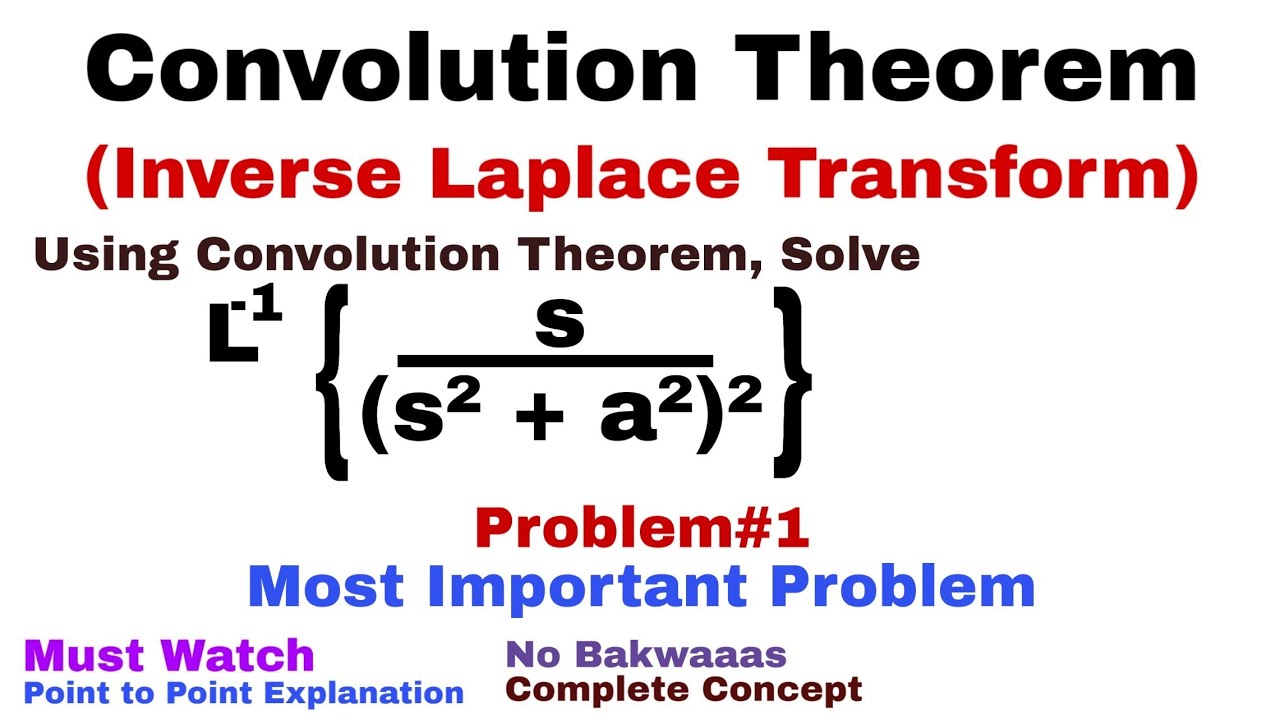
31 Convolution Theorem Complete Concept And Problem 1 Inverse Laplace Transform Youtube

Laplace Transform Of A Convolution Youtube

20 Convolution Theorem Problem 2 Inverse Laplace Transforms Youtube
No comments for "Convolution Theorem Laplace Transform Examples"
Post a Comment